What is a stye? This common yet often misunderstood eye condition affects many, appearing as a red, painful lump near the edge of the eyelid. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything from the causes and symptoms of styes to effective treatment options and preventive measures. Whether you’re currently experiencing a stye or simply want to learn how to prevent them, this post will provide you with valuable insights into maintaining optimal eye health.
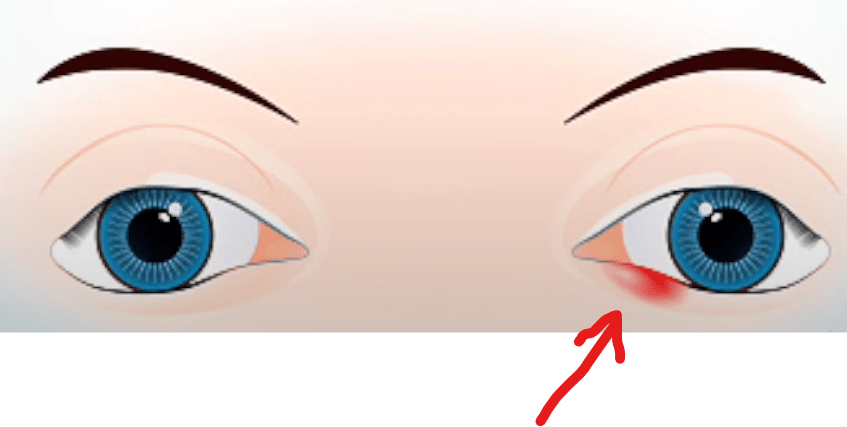
Table of Contents
Introduction to Stye
A stye, medically referred to as a hordeolum, is a common eye condition that appears as a red, painful lump near the edge of the eyelid. It may look similar to a pimple and is typically filled with pus. Styes are usually caused by a bacterial infection in the oil glands located at the base of the eyelashes. Although they can be uncomfortable and unsightly, styes are generally harmless and can be treated effectively at home.
Understanding Styes: Causes and Impact
Styes develop when bacteria, most commonly Staphylococcus aureus, invade and infect an eyelash follicle or oil gland. This leads to inflammation and the formation of a lump. While anyone can develop a stye, certain factors like improper eye hygiene, using outdated or contaminated makeup, and pre-existing skin conditions like rosacea or dermatitis can increase your risk.
Symptoms to Watch For
The most noticeable symptom of a stye is a swollen, red bump on the eyelid. Other symptoms can include pain, tenderness in the affected area, and watery eyes. Occasionally, a stye can cause the entire eyelid to swell, and in rare cases, multiple styes can appear simultaneously or recurrent styes can occur.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Most styes resolve on their own within a week or two. However, if you experience persistent pain, significant eyelid swelling, or changes in your vision, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended. Persistent or recurrent styes could indicate an underlying issue that requires medical intervention.
Causes of Stye
Understanding the causes of styes is essential for both prevention and treatment. A stye is typically triggered by a bacterial infection within the eyelid’s oil glands or hair follicles. Here are some primary factors that contribute to the development of this eye condition.
Bacterial Infection
The primary culprit behind styes is the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. This bacterium is commonly found on the skin but can cause problems when it enters the sensitive areas around the eyes. Infection occurs when these bacteria infiltrate the small oil glands of the eyelid, leading to inflammation and the formation of a stye.
Poor Eyelid Hygiene
Poor hygiene can increase the risk of developing styes. Not regularly washing the face or cleaning off makeup can allow bacteria to accumulate at the base of eyelashes, creating an ideal environment for stye development. Similarly, touching the eyes with dirty hands can transfer bacteria directly to the eyelids.
Use of Contaminated Makeup or Eye Products
Using outdated or contaminated eye makeup is a significant risk factor for stye formation. Bacteria can thrive in liquid makeup products, and using such contaminated items near the eyes can easily lead to infections.
Chronic Blepharitis
Blepharitis, a chronic inflammation of the eyelids, is closely associated with stye development. This condition leads to dandruff-like scales and a bacterial buildup along the eyelashes, increasing the likelihood of developing styes.
Other Risk Factors
Other conditions that may increase the risk include:
- Dry eyes or using contact lenses, which can irritate the eyelids and make them more susceptible to infection.
- Pre-existing dermatological conditions, such as rosacea or seborrheic dermatitis, which affect the skin’s oil glands and can contribute to stye formation.
This section explores the various causes of styes, emphasizing the importance of maintaining good eyelid hygiene and being cautious with eye-related products. It aims to provide readers with a clear understanding of how styes develop and the steps they can take to minimize their risk.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Identifying the symptoms of a stye and understanding the diagnostic process are crucial steps toward effective treatment. This section outlines the typical signs of a stye and how healthcare professionals diagnose this common eye condition.
Common Symptoms of Styes
Styes are characterized by several noticeable symptoms that can vary in intensity. The most common include:
- Redness and Swelling: The affected area of the eyelid becomes red and swollen, often resembling a pimple.
- Pain and Tenderness: Styes can be quite painful, especially when blinking or touching the eyelid.
- Tear Production: Increased tear production is a common reaction to the irritation caused by a stye.
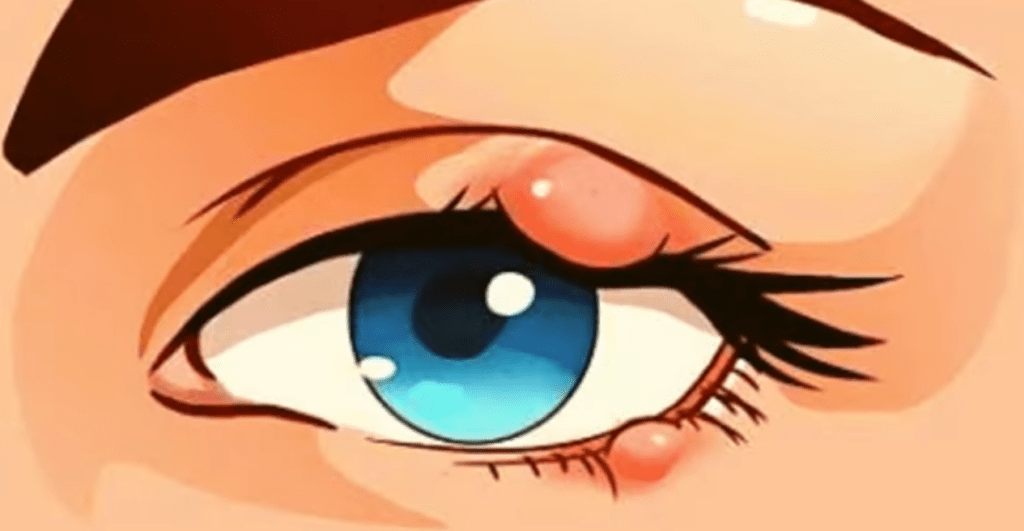
- Pus Accumulation: A visible pus point may appear at the center of the stye, indicating a buildup of infection.
- Sensitivity to Light: Some individuals may experience photophobia, or increased sensitivity to light, when they have a stye.
Diagnosing a Stye
Diagnosis of a stye is primarily based on a visual examination by a healthcare provider. Doctors look for the hallmark signs of redness, swelling, and pus accumulation to confirm the presence of a stye. In most cases, this visual inspection is sufficient for diagnosis. However, if styes recur frequently or are unusually persistent, further investigations may be necessary to rule out other underlying conditions, such as blepharitis or eyelid tumors.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
It is advisable to seek medical attention if:
- The stye does not start to improve within a few days or worsens.
- You experience severe pain or significant eye or eyelid swelling.
- You encounter changes in your vision or excessive discharge from the eye.
This section aims to educate readers on recognizing the symptoms of a stye and the importance of proper diagnosis. By understanding what to look for and when to seek help, individuals can better manage this condition and prevent complications.
Treatment Options for Stye
Effectively managing a stye involves a combination of home remedies and, if necessary, medical treatments. This section explores the various approaches to treating a stye, helping to alleviate discomfort and speed up the healing process.
Home Remedies
Most styes can be treated at home with simple, non-invasive methods:
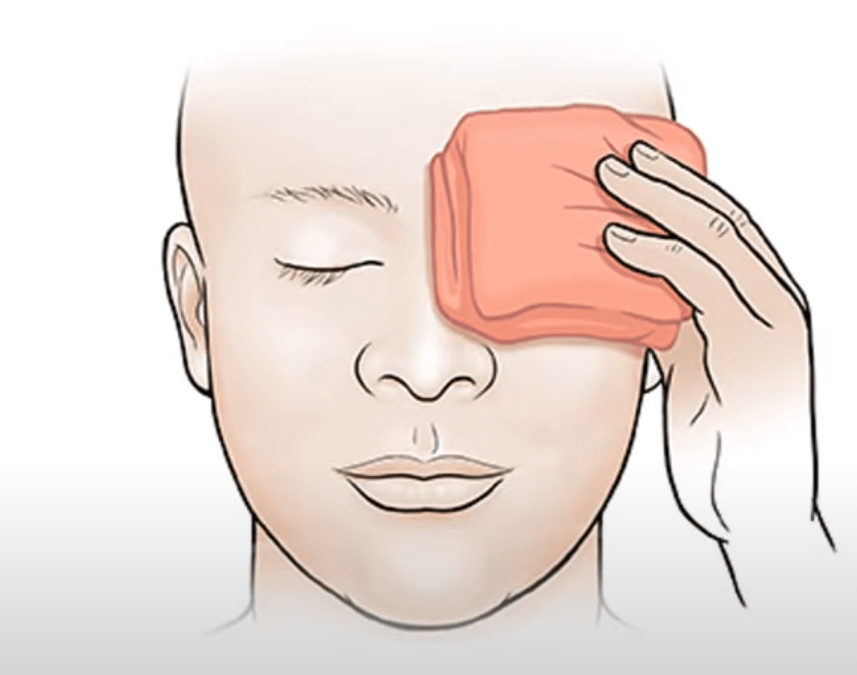
- Warm Compresses: The most recommended treatment is applying a warm compress to the affected eyelid. This helps the stye drain naturally and reduces swelling and pain. Use a clean, warm cloth and hold it against the eyelid for 10-15 minutes, several times a day.
- Keep the Area Clean: It is crucial to keep the eyelid clean and free from irritants. Use mild soap and water or suitable eyelid wipes to gently cleanse the area.
- Avoid Makeup and Contact Lenses: While experiencing a stye, avoid wearing eye makeup or contact lenses, as these can aggravate the condition and delay healing.
Medical Treatments
If a stye does not improve with home remedies or if it becomes particularly severe, medical intervention may be necessary:
- Antibiotic Ointments: A doctor may prescribe topical antibiotics to apply directly to the eyelid to help combat the infection.
- Steroid Injections: For particularly stubborn styes, a steroid injection may be used to reduce swelling.
- Surgical Drainage: In rare cases where a stye does not resolve on its own, a doctor might perform a minor procedure to drain the stye.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare professional if:
- The stye does not start to improve within 48 hours of home treatment.
- You experience significant pain or visual impairment.
- The redness and swelling spread beyond the eyelid.
This section provides a detailed guide on how to treat a stye, focusing on both home remedies and professional medical treatments to ensure effective management of the condition.
Prevention Tips
Preventing styes involves maintaining good eye hygiene and making a few lifestyle adjustments. Here are practical tips to reduce the risk of developing styes and to promote overall eye health.
Maintain Proper Eyelid Hygiene
- Clean Your Eyelids Regularly: Use a gentle cleanser or special eyelid cleaning wipes to remove dirt and bacteria from the eyelids. This is especially important if you are prone to eye infections or have conditions like blepharitis.
- Remove Makeup Before Sleeping: Always remove eye makeup thoroughly before going to bed to prevent bacterial buildup on your eyelids.
Manage Contact Lenses Carefully
- Handle with Clean Hands: Always wash your hands before touching contact lenses to avoid transferring bacteria to your eyes.
- Follow Lens Care Instructions: Use the correct lens solutions and replace your contact lenses as recommended to minimize the risk of eye infections.
Avoid Sharing Eye Products
- Personalize Eye Care Items: Never share towels, washcloths, eye drops, or makeup with others, as this can spread bacteria.
Dietary and Lifestyle Considerations
- Stay Hydrated and Eat Well: A healthy diet rich in vitamins A and D can promote eye health. Staying hydrated helps maintain the moisture balance in your eyes, reducing the risk of dryness and irritation.

- Manage Stress: High stress can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections, including those affecting the eyes.
When to Replace Makeup
- Monitor Makeup Shelf Life: Regularly replace eye makeup products like mascara and eyeliner every 3-6 months to avoid bacterial contamination.
Implementing these preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing styes and help maintain healthy eyes.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing styes is key to maintaining good eye health. This guide has outlined the essential aspects of styes, from identifying their causes and recognizing symptoms to exploring effective treatment options and adopting preventive measures. By incorporating these practices, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing styes and ensure your eyes remain healthy and comfortable.
Remember, while styes are generally not serious, persistent or particularly painful styes should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. Embracing good eyelid hygiene, being cautious with eye-related products, and following the outlined preventive tips can help you avoid this common yet bothersome eye condition. Your eyes are vital—taking good care of them helps you maintain not just your vision but also your overall quality of life.
Summary Table
Below is the summary table for the blog post points, outlining the key aspects of understanding and managing styes:
| Sr No. | Point Name | Brief Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Introduction to Styes | Explains what styes are, their typical appearance, and general information about their occurrence. |
| 2 | Causes of Styes | Discusses factors like bacterial infections and poor hygiene that lead to the development of styes. |
| 3 | Symptoms and Diagnosis | Outlines common symptoms of styes and how they are diagnosed by healthcare professionals. |
| 4 | Treatment Options | Details home remedies and medical treatments available for managing styes. |
| 5 | Prevention Tips | Provides practical tips on how to prevent styes through proper hygiene and lifestyle adjustments. |
| 6 | Conclusion | Summarizes the importance of understanding, managing, and preventing styes for maintaining eye health. |
This table serves as a quick reference for readers to understand the structure and content of the blog post on styes.




Pingback: How to Get Rid of a Stye Fast: Effective Remedies and Expert Tips - Digital Digest
Pingback: Are Styes Contagious? Expert Insights into Causes, Spread, and Effective Remedies - Digital Digest